|

Statistics Functions
One Attribute
count
|
Returns the number of cases for which the expression is true. For example, count(NumberOfPets > 0) will return the number of cases for which NumberOfPets is greater than zero. Similarly, count(exists(Gender)) will return the number of cases for which the attribute Gender is defined. count( ) returns the number of cases in the collection. For an attribute whose values are true and false, count will return the number of cases for which the value is true.
|
first
|
Returns the first value in the data set for the given attribute; for example, first(height) would be 61 for a collection of people in which the first person's height is 61 inches.
|
iqr
|
Interquartile range, for example, iqr(blood_pressure). This function returns the value at the 75th percentile minus the value at the 25th percentile.
|
last
|
Returns the last value in the collection for the given attribute; for example, last(name) would be Zelda for a collection of ducks in which the last duck's name is Zelda.
|
max
|
Maximum value; for example, max(age).
|
mean
|
The arithmetic mean; for example mean(height).
|
median
|
The median; for example, median(speed).
|
min
|
Minimum value; for example, min(salary).
|
percentile
|
Returns the value with a given percentile. For example, percentile(50, speed) is another way to compute the median. Or percentile(95, score) will return the score corresponding to the 95th percentile.
|
popStdDev
|
The standard deviation of the attribute you give it. This is the "population standard deviation."
|
popVariance
|
The variance of the values. This is also popStdDev squared.
|
proportion
|
Gives the proportion of cases for which the argument is true. For example, if 12 out of 24 people are over 12 years old, proportion(age > 12) will yield 0.5.
|
Q1
|
The value that lies at the 25th percentile; for example, the first quartile.
|
Q3
|
The value that lies at the 75th percentile; for example, the third quartile.
|
sampleStdDev
|
Computes the sample standard deviation according to the formula 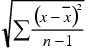 . It is an unbiased estimate of the population standard deviation. For example, sampleStdDev(pressure) computes the sample standard deviation of the attribute pressure. . It is an unbiased estimate of the population standard deviation. For example, sampleStdDev(pressure) computes the sample standard deviation of the attribute pressure.
|
sampleVariance
|
Computes the square of the sample standard deviation according to the formula 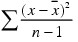 . For example, sampleVariance(voltage) computes the sample variance of the attribute voltage. . For example, sampleVariance(voltage) computes the sample variance of the attribute voltage.
|
stdDev
|
Standard deviation; for example, stdDev(score). Computes the standard deviation of the cases in the collection using the formula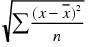 . .
|
stdError
|
Returns the standard error; for example, stdError(score). The formula that is used is 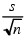 where s is the sample standard deviation and n is the number of cases. where s is the sample standard deviation and n is the number of cases.
|
sum
|
Returns the sum of the values over all the cases. For example, sum(time)/count(isNumber(time)) is another way to compute the mean of the attribute time.
|
uniqueValues
|
The number of unique values that an attribute has in the data set. For example, uniqueValues(sex) will be 2 if there are only two values ("male" and "female") for sex. (Missing values are ignored.)
|
variance
|
Computes the variance of an attribute, that is, the square of the standard deviation, according to the formula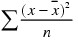 . For example, variance(before - after) computes the variance of the difference of the two attributes before and after. . For example, variance(before - after) computes the variance of the difference of the two attributes before and after.
|
Transformations
bin
|
Takes the form bin(a, bin, min, max) where a = attribute, bin = bin width, min = start of bin 1, and max = end. bin gives you a string (category value) for a (its "bin" as defined by the other arguments). For example, bin(3.14, 2, 0, 10) gives "b02" because the value (3.14) is in bin 2 in [0, 10] with bins of width 2. (The last two arguments are optional.)
|
next
|
The value for the next case. If this is the last case, next returns 0. For example, next(year) returns, for each case, the value of the next year. As with prev, next takes an optional second argument that specifies the value to be returned for the last case.
|
popZScore
|
Returns the number of population standard deviations a value is from the mean. For example, popZScore(finalExam) computes a standard score for each value of the attribute finalExam.
|
prev
|
The value for the previous case. If this is the first case, prev returns 0. For example, prev(year) returns, for each case, the value of the previous year. An optional second argument allows you to specify the value prev should take if there is no previous case. For example, prev(Factor, 1) will return the previous value of Factor for all cases except the first, for which it returns 1.
|
rank
|
Returns the position of the value when cases are ordered from lowest to highest. For example, rank(Population) used as an attribute in a collection of states assigns to each state its rank according to population. Note that if there are duplicate values, the rank will be fractional and the same for all the values. See also uniqueRank.
|
runLength(flip)
|
This one's wild! It gives the number of identical values immediately prior to and including the current value. For example, if flip contained {H, H, H, T, H, T, T}, this example would return {1, 2, 3, 1, 1, 1, 2}. You can use max(runLength(flip)) to compute the longest streak of heads or tails in a coin-flipping simulation.
|
sampleZScore
|
Returns the number of sample standard deviations a value is from the mean. For example, sampleZScore(height) computes a standard score for each value of the attribute height.
|
uniqueRank
|
Returns the unique position of a value in a list of values sorted from smallest to largest. Each value in the list gets assigned a different rank, even if there are duplicate values. For example, if the attribute N contains the values {1, 2, 3, 2}, an attribute using the expression uniqueRank(N) will have values {1, 2, 4, 3}. See also rank.
|
zScore
|
Same as sampleZScore.
|
Two Attributes
correlation
|
Returns the correlation coefficient for two continuous attributes. For example, correlation(stories, height) will return the correlation coefficient for stories and height. This value will be between -1 and +1 and is a measure of how closely the values of one attribute follow those of the other.
|
covariance
|
Returns the average of the products of the deviations of each of two attributes from the mean. For example, covariance(hp, mpg)/variance(hp) would give the slope of the least-squares regression line for hp versus mpg.
|
linRegrIntercept
|
Returns the intercept of the least-squares regression line with x as the independent attribute and y as the dependent attribute.
|
linRegrSlope
|
Returns the slope of the least-squares regression line with x as the independent attribute and y as the dependent attribute.
|
rSquared
|
The square of the correlation coefficient for two attributes. rsquared(x, y) represents the proportion of the variation of y that is accounted for by the variation in x. It takes on values between 0 and 1.
|
Also see Special Functions.
TinkerPlots Help
© 2012 Clifford Konold and Craig D. Miller
|
|





